Electric Power Systems: A Guide to the Grid That Powers Our World
2025-04-30
What are Electric Power Systems?
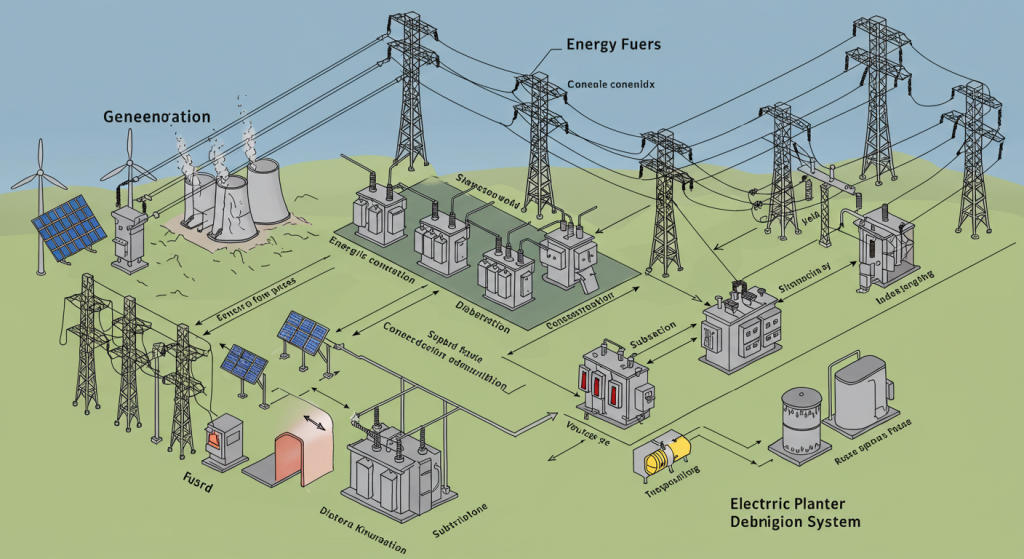
Electric power systems are groups of people and technology that work together to provide electricity by producing it, transmitting it, distributing it, and finally, using it. They allow for the safe delivery of electricity from power plants to people’s homes, businesses, and factories.
An electric power system consists of four primary components:
1. Generation
2. Transmission
3. Distribution
Utilization (Consumption)
Each stage plays a critical role in the delivery of reliable and stable electrical power.
Power Generation: Changing Energy Into Electricity
Electricity starts at the generation stage, where electric energy systems convert different types of fuels into electrical energy.
Key Generation Types:
• Fossil Fuel Power Plants: They burn coal, natural gas, and oil to produce steam that drives turbines.
• Nuclear Power Plants: They use nuclear fission to produce heat and electricity.
• Renewable:
o Solar Power: It converts sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells.
o Wind Energy: Wind turbines create electricity using wind.
o Hydropower: Moving water generates electricity.
o Geothermal Energy: It produces electricity from heat found inside the Earth.
Power Transmission: Transporting Electrical Energy Across Great Distances
Following generation, electrical power is transmitted through high-voltage power lines.
Key Components:
• Transmission Towers: High-voltage telecommunication towers that transmit power over great distances.
• Substations: These either raise or lower the voltage so electricity can be easily transmitted.
• HVDC Systems: Efficient long-range transmission of electricity uses High Voltage Direct Current.
• Flexible AC Transmission Technologies: boost system control and electric power transfer.
Why High Voltage?
Allows the current to be lower, therefore, power loss during transport over great distances is lower. Electricity grids frequently cover nations. The reason is that interconnected networks of grids are fundamental for dependable service.
Power Distribution: Distributing Electric Power to Consumers
Once the electricity is transmitted, the voltage is reduced at distribution substations and is then supplied to distribution networks.
Types of Distribution Systems:
• Radial Networks: These are easy to build but very sensitive to faults.
• Loop Networks: Great for providing redundancy.
• Smart Grids: Digital Communication reprimanding intelligent real-time monitoring enjoys power over the network.
• Microgrids: Energy systems that can stay independent from the main grid but are local.
Distribution lines directly provide electricity to residential, commercial, and industrial users. Voltage control and network reconfiguration help maintain balance and stability during load changes.
Power Utilization: How We Use Electricity?
Residences, factories, and offices are powered through the industrial and residential systems, supplying electric power.
Aspects of Utilization include:
• Electric Load: The total power consumption at any instant.
• Energy Efficiency: Using a lesser amount of power while still achieving the required output.
• Demand Response: Change in electricity consumption during peak periods to help stabilize the grid.
• Electric Vehicles (EVs): These are now becoming more integrated into the grid as storage and load.
Smart Grids and Emerging Technologies
Digital tools are being used to upgrade existing grids into smart grids. These advancements improve the flexibility, reliability, and balance of the grid.
Smart Grid Features:
• Real-time tracking using IoT sensors
• Automated Fault Identification
• Adoption of renewable resources
• Two-way power exchange with decentralized energy systems
• Active engagement of customers using smart meters
Microgrids and Nanogrids
• Microgrids: Power communities, campuses, or islands. Can function independently from the main grid.
• Nanogrids: Power single buildings or small facilities.
These smaller systems offer increased resilience during blackouts or other disaster scenarios.
Power Electronics and Equipment
Advanced hardware is essential for reliable electric power systems.
Critical Equipment:
• Power Transformers: Voltage adjustment (up/down)
• Circuit Breakers: Eliminate faults
• Switchgear: Controls and protects electrical components.
• Protective Relays: Triggers circuit breakers if abnormal conditions are detected.
• Harmonic Filters: Elimination of distortion improves waveform quality.
To guarantee maximum operational efficiency of the grid, high-performance equipment must be deployed.
Energy Storage and Renewables Integration
With the increasing importance of renewable energy, the electricity grid has to cope with integrating power sources of varying reliability.
Integration challenges:
• Renewable energy generation
•Generation shifting up and down frequently
• Voltage inconsistencies
Solutions:
Reserve capacities of added capacity (flexible generation) – ESS stores power to be accessed during demand surges.
Lithium and ion technologies, flow batteries, and solid-state.
Storage capable of holding hydrogen energy: store electricity to convert it to hydrogen through electrolysis.
Electricity Regulation and Market Components
Electric power systems are functioning in the context of open market systems with many participants.
Elements of the Market:
• The price of electricity in a region is set according to demand as well as supply, and generation costs.
• Real-time and day-ahead trading.
• Control of frequency and reserve power is are ancillary service.
• Regulation and Policy:
To encourage the incorporation of renewable sources into energy systems, modernize grid infrastructure, and improve consumer adequacy, governmental policies are enacted.
Electric Power Systems Buying Guide
Identify Why You Need Power
You need power systems for different use cases, such as residential homes, businesses, or even industrial complexes. Understanding these categories makes it simple to estimate energy consumption, load, and backup requirements.
Select Preferred Methods of Power Generation
From renewable sources like wind, solar, or hydroelectric power to traditional fossil fuels and even nuclear power. With increasing popularity these days, renewable sources tend to have fewer overall financial implications in the long run.
All-Inclusive Components of the Electrical System
• Supplying Energy with Generators and/or Solar panels
• Storage and Capacity Reservoir
• Power Delivery with Substations and Transmission Lines
• Voltage Regulation using Switchgear and Transformers
Take note that power components have different factors to consider, such as safety, reliability, and overall trustworthiness.
Find Systems with Smart Capabilities
For better functionalities, look out for smart grids that enable monitoring and controlling. Include features demand response, energy efficiency, SCADA control, and unit integration.
Hire Professional Acquaintances for the Job
For a customized power solution, such as transmission towers, distribution structures, and even substation hardware, suppliers such as XY TOWER come in handy.
Conclusion
From the coffee machine in the morning to life-saving hospital equipment, reliable electricity helps power many crucial devices. Meeting these requirements demands a sophisticated and resilient electric power system, which it certainly does for national security, economic development, and overall public welfare. At XY TOWER, we ensure your energy infrastructure is optimized from smart grid components to transmission towers, substation structures, and more. Visit our homepage for more.

Hey, I’m Chunjian Shu
"X.Y. Tower: Reliable, innovative solutions for high-quality towers and electrical equipment with professional service.
